- Products
- Areas of application
- The Graphite
- Properties of graphite
- Features
- The expansion graphite
- Properties of expansion graphite
- Advantages of expansion graphite
- Expansion graphite as fire resistant material
- Technical datas about Grafit Kropfmünk AG`s most common materials
- Material selection


Areas of application
- Building industry
- Thermal conduction and insulation
- Against electric charge
- Fire protection
- Powder Metallurgy
- Lubricants, carbon brushes
- Heat resistant applications, casting jars
- Energy products: fuel cells, Li-ion and polymer batteries, alkaline batteries
- Pencils, polymer applications and dispersions
- Hot forming (forging)
Main users in Hungary: Forging plants, catalyst manufacturers, fire protection paint manufacturers, carbon profile manufacturers, rubber factories.
The Graphite
Carbon occurs in large quantities in the sun and in the atmosphere of most planets. On Earth, although its incidence is less than 0.1%, organic compounds are even the basis of life itself. This is due to the fact that it is happy to form compounds both with itself and with other elements such as oxygen, hydrogen or nitrogen. Four allotropic occurrences of carbon crystals are known: Graphit, Diamond, Fullerenes, Nanotubes

Properties of graphite:
Excellent conductivity
The excellent thermal and electrical conductivity of graphite is due to the free electrons. This property is highly dependent on the size and location of the crystals.
Outstanding lubricating properties
The excellent lubricating property of graphite is due to the layers of crystal lattice that move easily on top of each other. It retains its advantageous properties even under high temperature and pressure conditions.
Protection against oxidation and repetitive heat shock
Due to its crystal structure properties, graphite is excellent in resistance to oxidation and most chemicals, which is why it is preferred for refractory materials.
Component of host compounds
Due to the bond strength between the structural layers of graphite, graphite is suitable for storing certain molecules in its lattice structure. It is this storage capacity that makes it suitable as a lubricant or in the manufacture of rechargeable batteries.
EXPANSION (VOLUME INCREASE, EXPANDING) GRAPH
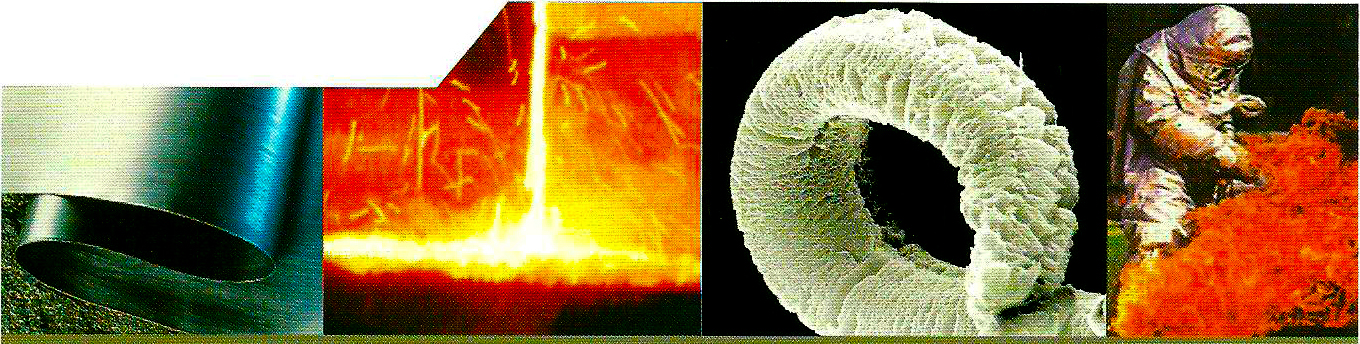
Because graphite has a layered structure, atoms and tiny molecules can also be introduced between the carbon layers. (Intercalation)
During the process, a so-called expansion graphite salt or GIC (Graphite Intercalation Compound) intercalation graphite compound is formed. This type of graphite, which is remarkably large and has a large volume, contains a high proportion of intercalation layers.
Sulfur or nitrogen compounds are commonly used as intercalation mediators. As a result of the heat, the layers become separate as an accordion, and thus the volume of the graphite plates increases, expands, i.e. expands.
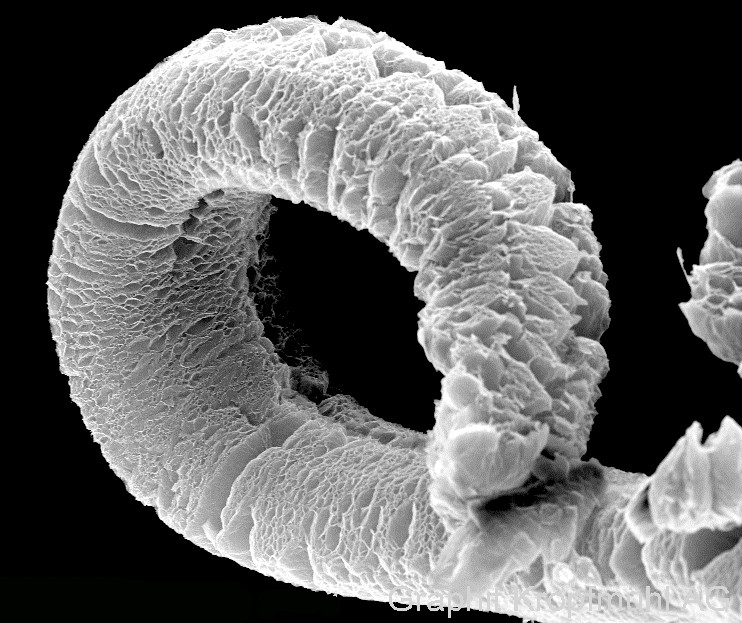
Depending on the type of material, the volume increase can start as early as 180Co, a process that happens suddenly and quickly. If the volume increase is free, then the final volume can be several hundred times the original extent.
The properties of the expansion graphite, such as the initial temperature required to initiate volume growth and the degree of expansion, are primarily determined by the intercalation quality (i.e., the amount of intercalation layers) and the intercalation mediator.
EXPANSION GRAPHITE AS AN ANTI-INFLAMMATOR / REFRACTORY MATERIAL
One of the primary properties of expansion graphite is that it is refractory and is therefore primarily used as an anti-inflammatory material. As a result of fire and heat, graphite expands to form a thickened layer on the surface of the materials.
This retains and prevents the spread of fire, while minimizing one of the most dangerous consequences of combustion, smoke and the formation of toxic gases.